Each bearing type has charateristic properties that make it more or less suitable for use in a given application. When selecting a bearing type, you should consider factors below.
Allowable bearing space
The allowable space for bearings is generally limited. In most cases, shaft diameter (or the bearing bore diameter) has been determined according to the machine's other design specifications. Therefore, bearing's type and dimensions are determined according to bearing bore diameters. For this reason all dimension tables are organized according to standard bore diameters. There is a wide range of standardized bearing types and dimensions: the right one for a particular application can usually be found in these tables.
For rolling bearings, there are numerous standardized dimension series and types, and the selections of the optimum bearing from among them is necessary. The picture below shows the dimension series of radial bearings and corresponding bearing types.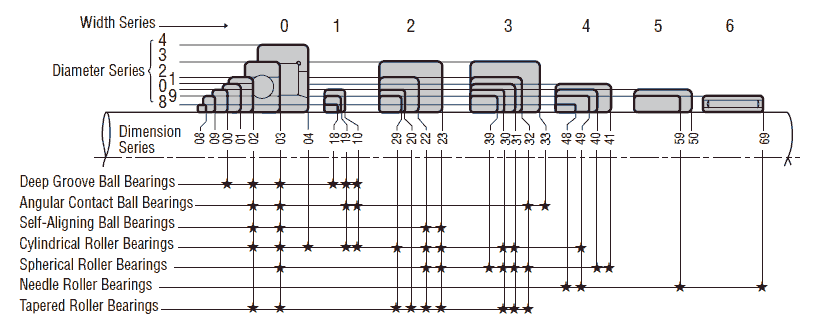
Bearing load
The characteristics, magnitude, and direction of loads acting upon a bearing are extremely variable. In general, the basic load ratings shown in bearing dimension tables indicate their load capacity. However, in determining the appropriate bearing type, consideration must also be given to whether the acting load is a radial load only or combined radial and axial load, etc. When ball and roller bearings within the same dimension series are considered, the roller bearings have a larger load capacity and are also capable of withstanding greater vibration and shock loads. The picture below shows the load carrying capacity of a bearing.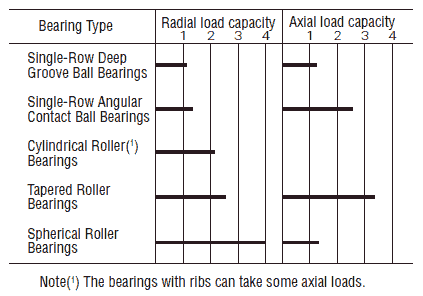
Operating speed, maximum speed
The permissible operating temperature of rolling bearings imposes limits on the speed at which they can be operated. The operating temperature is determined, to a great extent, on the frictional heat generated in the bearing, except in machines where process heat is dominant.
When selecting bearing type on the basis of operating speed, you should consider the following:
- Ball bearings have a lower frictional moment than same-sized roller bearings.
- Thrust bearings cannot accommodate speeds as high as same-sized radial bearings.
- Single row bearing types typically generate low frictional heat and are therefore more suitable for high-speed operation than double or multi-row bearings.
- Bearings with rolling elements made of ceramics (hybrid bearings) accommodate higher speeds than their all-steel equivalents.
Bearing tolerances
The dimensional accuracy and operating tolerances of bearings are regulated by ISO and JIS standards. For equipment requiring high tolerance shaft runout or high speed operation, bearings with Class 5 tolerance or higher are recommended. Deep groove ball bearings, angular contact ball bearings, and cylindrical roller bearings are recommended for high rotational tolerances.
Misalignment of inner and outer rings
Because of deflection of a shaft caused by applied load, dimensional error of the shaft and housing, and mounting error, the inner and outer rings are slightly misaligned. Bearing types vary in their ability to compensate for misalignment between the shaft and housing:
- Self-aligning bearings
Self-aligning bearings can compensate for misalignment within the bearing. - Alignment bearings
Alignment bearings can accommodate initial static misalignment because of their sphered outside surface. - Rigid bearings
Rigid bearings (deep groove ball bearings, angular contact ball bearings, cylindrical, needle and tapered roller bearings) accommodate misalignment within the limits of their internal clearance. For rigid bearings, any misalignment may reduce service life.
Stiffness
The stiffness of a rolling bearing is characterized by the magnitude of the elastic deformation in the bearing under load and depends not only on bearing type, but also on bearing size and operating clearance.
When selecting bearing type on the basis of stiffness requirements you should consider, for bearings with the same size, that:
- Stiffness is higher for roller than ball bearings
- Stiffness is higher for full complement bearings than for the corresponding bearing with a cage
- Stiffness is higher for hybrid bearings than for the corresponding all-steel bearing
- Stiffness can be enhanced by applying a preload
Mounting and dismounting
Separable types of bearings like cylindrical roller beraings, needle roller bearings and tapered roller bearings are convenient for mounting and dismounting. For machines in which bearings are mounted and dismounted rather often for periodic inspection, these types of bearings are recommended. Also, self-aligning ball bearings and spherical roller bearings (small ones) with tapered bores can be mounted and dismounted relatively easily using sleeves.
Noise and torque levels
Rolling bearings are manufactured and processed according to high precision standards, and therefore generally produce only slight amounts of noise and torque. For applications requiring particularly low-noise or low-torque operation, deep groove ball bearings and cylindrical roller bearings are most appropriate.
Integral sealing
There are two reasons for sealing bearings or bearing arrangements:
- Keeping the lubricant in the bearing, and avoiding pollution of adjacent components
- Protecting the bearing from contamination, and prolonging bearing service life
Capped bearings (sealed bearings or bearings with shields) can provide cost-effective and space-saving solutions for many applications.
Cost and availability
After determining your required bearing type, you may find it beneficial to select an appropriate bearing from popular items, because popular items have a high level of availability and generally provide a cost-effective solution.
