Integral sealing (including shields and seals) can significantly prolong bearing service life, because it keeps lubricant in the bearing and contaminants out of it. Usually, seal and shield type bearings are maintenance-free, and are used to protect the bearing from contaminants. 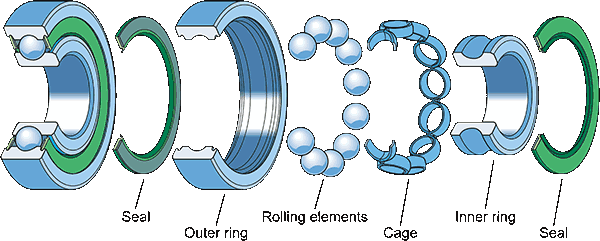
Numerous reputable manufacturers offer shield bearings and rubber seal bearings. How should we decide whether to use sealed bearings or those with shields?
Shield bearings
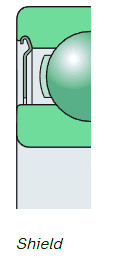
There is a small gap between the shield and inner ring in a shield bearing. Bearings fitted with shields are used where the operating conditions are relatively clean, or where low friction is important because of speed or operating temperature considerations.
Bearings with seals
Usually, Bearings with seals are preferred for arrangements where contamination is moderate. Bearings with rubber seals are generally available in the following types:
Bearings with contact seals
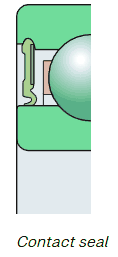
The contact seal designed for maximum protection against all contaminants. The lip seal is pressed against the surface of the inner ring. It gives excellent dust and water protection. With lower speed and temperature lists, The contact seal bearings are used in situations where maximum sealing is critical.
Bearings with low-friction seals
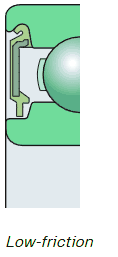
The low-friction seals are designed for excellent contamination protection when torque levels are a consideration. Lower friction levels than the contact seal but designed for use in high contaminant environments.
Bearings with non-contact seals
The non-contact seals are designed for the higher speed, higher temperature requirements of applications such as electric motors. The non-contact seal bearing can be operated at the same speeds as shield bearings, but it has better sealing capability than a shield bearing. It has an extremely narrow gap with the inner ring shoulder.
Selection guidelines for shielded and seal bearings
Selection guidelines for shield and different seals under various operating conditions are listed below.
| Requirement | Shields | Non-contact seals | Low-friction seals | Contact seals |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low friction | Best | Best | Very good | Fair |
| High speed | Best | Best | Very good | Fair |
| Grease retention | Fair | Good | Very good | Best |
| Dust exclusion | Fair | Fair | Good | Best |
| Water exclusion | Not recommended | Not recommended | Fair | Best |
Designation suffix for shield and seals
Different shield or seals are indicated by different suffixes.
| Brand | Designation suffix | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shields | Non-contact seals | Low-friction | Contact seals | |||||
| on one side | on both sides | on one side | on both sides | on one side | on both sides | on one side | on both sides | |
| SKF | Z | 2Z | RZ | 2RZ | RSL | 2RSL | RSH, RS1 | 2RSH, 2RSH1 |
| NSK | Z | ZZ | V | VV | DW | DDW | DU | DDU |
| NTN | Z | ZZ | LB | LLB | LH | LLH | LU | LLU |
| FAG | Z | 2Z | RZ, BRS | 2RZ, 2BRS | RSR, HRS | 2RSR, 2HRS | ||
| TIMKEN | Z | ZZ | RZ | 2RZ | RS | 2RS | ||
Regarding more information about the bearing number meaning, please refer to the article below:
- SKF bearing designation
- FAG bearings nomenclature
- NSK bearing nomenclature
- NTN prefixes and suffixes code
